Lactic Acidosis: Causes, Risks, and What You Need to Know
When your body produces too much lactic acidosis, a dangerous buildup of lactic acid in the bloodstream that disrupts pH balance. It’s not just a lab result—it’s a signal your cells aren’t getting enough oxygen or are under severe stress. This isn’t something that happens overnight. It usually shows up when something else is seriously wrong—like a heart attack, severe infection, or uncontrolled diabetes.
One of the biggest triggers is metformin, a common diabetes drug that can increase lactic acid production in people with kidney or liver problems. Metformin is safe for most, but if your body can’t clear it properly, lactic acid starts piling up. That’s why doctors check kidney function before prescribing it. oxygen therapy, used to support breathing in chronic lung disease or after trauma can help prevent it by giving your cells the oxygen they need to burn fuel cleanly. Without enough oxygen, your body switches to a backup energy system that churns out lactic acid as waste.
People with metabolic disorders, conditions that mess with how your body turns food into energy are also at higher risk. Think liver failure, severe anemia, or even intense, unaccustomed exercise. Alcohol abuse? That’s another red flag. The liver can’t process lactate properly when it’s busy detoxing alcohol. Even a short bout of shock or sepsis can trigger it—your tissues are starving for oxygen, and lactic acid floods in.
Symptoms are subtle at first: nausea, fatigue, rapid breathing. Then it gets worse—muscle weakness, confusion, low blood pressure. Left untreated, it can crash your heart and lungs. It’s not a condition you wait out. If you’re on metformin and suddenly feel off, especially with vomiting or dizziness, get checked. A simple blood test can spot high lactate levels before it turns critical.
What you’ll find in the posts below aren’t just random articles. They’re real-world connections to how lactic acidosis shows up in daily health struggles—whether it’s from diabetes meds, oxygen shortages in chronic lung disease, or how kidney function plays a silent role. You’ll see what actually puts people at risk, how doctors spot it early, and what steps can help prevent it. No fluff. Just what matters when your body’s chemistry is tipping out of balance.
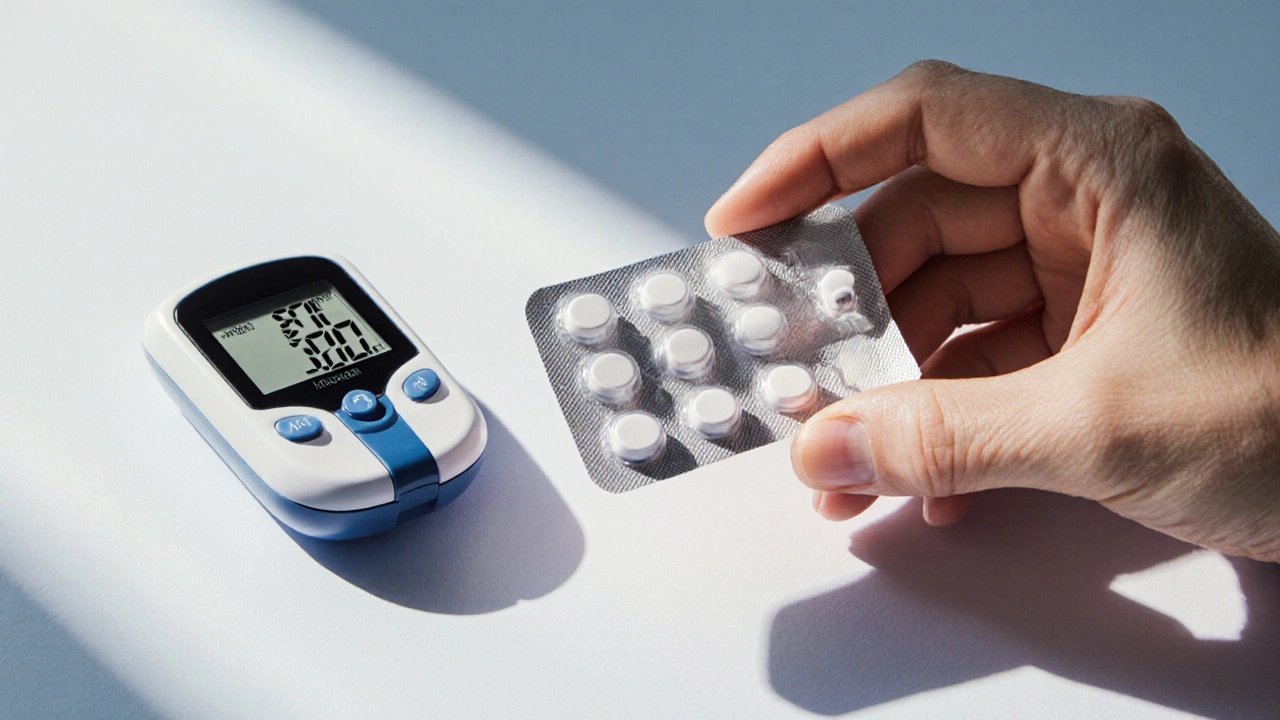
Metformin Side Effects: Why It Can Be Harmful
•26 Oct 2025
Explore why metformin can cause problems, from common stomach upset to rare lactic acidosis, and learn how to use it safely with clear guidelines and FAQs.